Lower back pain is a common issue that affects people of all ages and lifestyles. For many, it can be an occasional nuisance, but for others, it can become a chronic problem that impacts daily activities, work, and overall quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management techniques for lower back pain can help you take steps toward relief and prevent further complications.
Dr. Kritesh Mishra, a Joint Replacement & Sports Injury Specialist, offers valuable insights and expert care for those struggling with lower back pain and related issues.
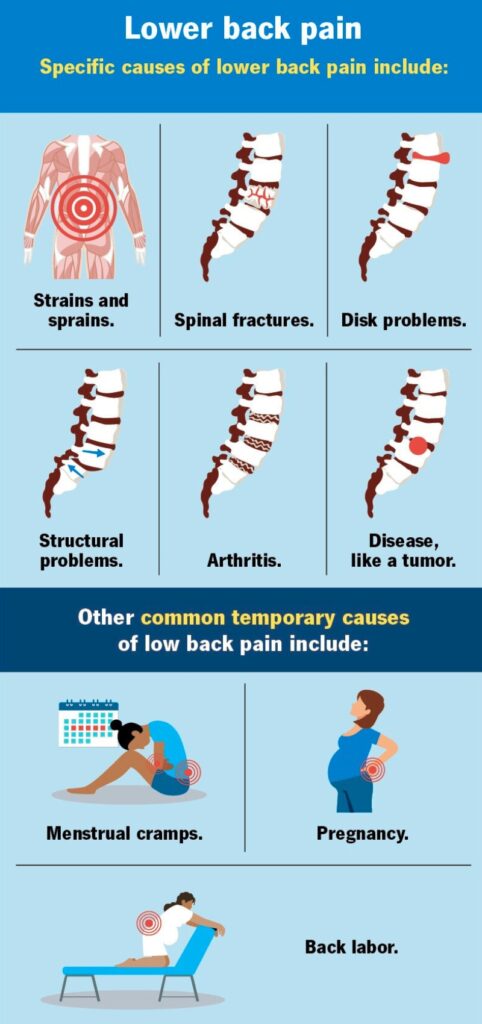
What Causes Lower Back Pain?
Lower back pain can arise from various factors, such as injury, lifestyle, or medical conditions. Some common causes include:
Muscle or Ligament Strain: Overuse, improper lifting, or sudden awkward movements can strain muscles and ligaments in the lower back. This is often one of the most frequent causes of back pain, especially in people who work in physically demanding jobs or engage in sports.
Herniated Disc: The discs between our vertebrae provide cushioning and flexibility. However, these discs can sometimes bulge or rupture, pressing on nearby nerves and causing pain. This is particularly common in the lumbar, or lower back, region.
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis can affect the lower back, leading to stiffness, pain, and decreased mobility. Arthritis in the spine may narrow the space around the spinal cord, a condition called spinal stenosis.
Poor Posture: Many people develop lower back pain due to poor posture, especially those who spend long hours sitting or standing in the wrong position.
Other Medical Conditions: Kidney problems, infections, and even certain types of cancer can sometimes cause back pain. It’s essential to understand the underlying cause to determine the best course of action.
Symptoms
The symptoms of lower back pain vary depending on the cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Aching or Stiffness: Persistent dull ache or stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity or sleeping.
- Sharp or Radiating Pain: Some people experience a sharp, stabbing pain that radiates down the legs, often associated with nerve compression.
- Limited Mobility: Pain or stiffness can restrict movement and make it difficult to perform daily tasks, such as bending, lifting, or standing.
- Muscle Spasms: In some cases, lower back pain can cause muscles to tighten or spasm, leading to sudden discomfort.
How to Manage Lower Back Pain
There are several approaches to managing lower back pain, depending on the severity of the pain and its underlying causes. Here are some effective methods:
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Staying active can help strengthen the muscles that support the lower back. Low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, or gentle stretching, can improve flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Maintain Proper Posture: Good posture while sitting, standing, and lifting can relieve strain on the spine. Consider adjusting your workspace, using ergonomic chairs, and keeping your spine aligned to support lower back health.
- Apply Heat or Ice: Applying ice packs to the lower back can reduce inflammation, while heat pads can relieve muscle tension. Alternating between ice and heat therapy can be especially beneficial in managing lower back pain.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can help alleviate lower back pain, but it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before relying on them long-term.
- Stay Mindful of Movements: Avoid sudden movements, especially bending or twisting, as these can worsen lower back pain. When lifting heavy objects, bend your knees and use your leg muscles instead of your back to lift.
When to Seek Medical Help
While many cases of lower back pain resolve with rest and home remedies, some instances require professional medical intervention. You should consider seeing a doctor if:
- The pain persists for more than a few weeks.
- You experience severe pain that doesn’t improve with rest.
- The pain radiates down your legs, indicating possible nerve involvement.
- You have a fever, weight loss, or weakness associated with the pain, as these could indicate an underlying condition.
Lower back pain can be managed effectively with a combination of preventive practices, exercises, and simple remedies. By understanding its causes and symptoms, you can take steps to alleviate pain and improve your quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of lower back pain?
Lower back pain can be caused by muscle strains, poor posture, disc issues, arthritis, and conditions like sciatica.
How can I relieve lower back pain at home?
Try low-impact exercises, maintain good posture, use heat or ice therapy, and take over-the-counter pain relievers as needed.
When should I see a doctor for lower back pain?
See a doctor if pain persists for more than a few weeks, radiates to the legs, or is accompanied by fever, weight loss, or weakness.
Can exercise help reduce lower back pain?
Yes, gentle exercises and stretches can strengthen back muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain over time.
How can I prevent back pain?
Practice good posture, avoid heavy lifting, stay active, and use ergonomic furniture to support your spine alignment.

