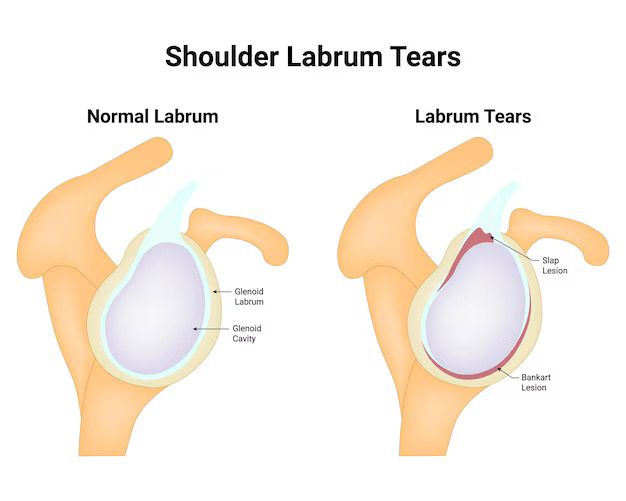
A Bankart tear is a common injury that affects the shoulder joint, particularly the labrum. It occurs when the labrum, a ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint, is torn due to trauma or overuse. This injury is most often seen in athletes or individuals who engage in repetitive overhead activities. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for a Bankart tear is essential for anyone experiencing shoulder instability or pain.
Causes of Bankart Tear
A Bankart tear is usually caused by shoulder dislocation. When the shoulder joint dislocates, the head of the arm bone (humerus) moves out of the socket (glenoid). This movement can cause the labrum to tear. There are several factors that contribute to it, including:
Trauma or Injury: A sudden fall on an outstretched arm, a direct blow to the shoulder, or an accident can result in shoulder dislocation, leading to a Bankart tear.
Repetitive Movements: Athletes involved in sports like basketball, volleyball, swimming, and weightlifting are prone to developing a Bankart tear due to the repetitive overhead motion of their arms. These repetitive motions can weaken the shoulder joint, making it more susceptible to injury.
Previous Shoulder Dislocation: Individuals who have had a prior shoulder dislocation are at a higher risk of developing a Bankart tear. The instability in the shoulder joint makes it easier for the labrum to tear again.
Symptoms of Bankart Tear
It often presents itself through a variety of symptoms, which can vary in severity depending on the extent of the injury. Some of the common symptoms include:
Shoulder Instability: Individuals with a Bankart tear may feel that their shoulder is loose or may experience frequent shoulder dislocations. This feeling of instability is particularly noticeable when lifting the arm above the head or rotating the shoulder.
Pain: Pain is one of the most common symptoms. It may worsen with certain activities, particularly those involving arm movement above the head or shoulder rotation.
Limited Range of Motion: A torn labrum can limit the ability to move the shoulder through its full range of motion. Reaching for objects, throwing, or lifting the arm may feel restricted or uncomfortable.
Clicking or Popping Sensation: Many individuals with a Bankart tear report a clicking, popping, or grinding sensation in the shoulder, especially when moving the arm in certain directions.
Weakness in the Shoulder: Due to the instability in the shoulder joint, individuals may experience muscle weakness or find it difficult to lift heavy objects.
Treatment Options for Bankart Tear
Treatment for a Bankart tear depends on the severity of the tear and the level of shoulder instability. Treatment options can be categorized into non-surgical and surgical approaches:
Non-Surgical Treatment
In mild cases, non-surgical treatment may be recommended. This approach focuses on managing symptoms, improving shoulder stability, and restoring range of motion.
Physical Therapy: A well-structured physical therapy program is often the first line of treatment. Strengthening exercises for the muscles around the shoulder can help stabilize the joint and reduce the risk of further dislocations. Therapy can also restore the shoulder’s full range of motion and improve overall function.
Rest and Activity Modification: Resting the shoulder and avoiding activities that strain the joint can give the labrum time to heal. Ice and anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
Surgical Treatment
If it is severe or if the shoulder continues to dislocate, surgery may be necessary to repair the torn labrum. Surgical options include:
Arthroscopic Surgery: Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure where small incisions are made, and a camera is inserted into the joint to guide the repair. The torn labrum is then reattached to the shoulder socket using small anchors.
Open Surgery: In some cases, open surgery may be required, especially if the tear is complex. The surgeon will make a larger incision to access the shoulder joint and perform the necessary repairs.
Post-surgery, physical therapy is essential to ensure proper healing and restore shoulder strength and mobility.
Conclusion
A Bankart tear can significantly impact your daily life and activities, particularly if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is key to managing this injury effectively. If you suspect you have a Bankart tear, consulting a specialist like Dr. Kritesh Mishra Joint Replacement & Sports Injury Specialist can provide a personalized treatment plan to restore your shoulder’s health and function.
Frequently Asked Questions
It is a tear in the labrum, the cartilage around the shoulder socket, often caused by shoulder dislocation or trauma.
Symptoms include shoulder instability, pain, limited range of motion, weakness, and sometimes a clicking or popping sensation.
Treatment can be non-surgical, involving physical therapy and rest, or surgical, such as arthroscopic surgery to repair the torn labrum.