An Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) injury is one of the most common knee injuries, especially among athletes and individuals involved in physically demanding activities. The ACL is a critical ligament that stabilizes the knee joint, and when it gets injured, it can lead to significant pain and mobility issues. In this blog, we’ll delve into what an ACL injury is, its causes, symptoms, and the available treatment options.
What is an ACL Injury?
The ACL is one of four main ligaments in the knee that connect the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). It plays a crucial role in stabilizing the knee, especially during activities that involve sudden changes in direction, jumping, or deceleration. An ACL injury typically occurs when this ligament is overstretched or torn, often due to sudden, forceful movements.
ACL injuries are classified into three grades:
- Grade 1 Sprain: The ligament is mildly damaged and slightly stretched but still able to keep the knee stable.
- Grade 2 Sprain: The ligament is stretched to the point where it becomes loose; this is often referred to as a partial tear.
- Grade 3 Sprain: The ligament is completely torn into two pieces, and the knee becomes unstable.
Causes of ACL Injury
ACL injuries are common in sports like soccer, basketball, football, and skiing, where there are rapid changes in movement, sudden stops, and jumps. Some of the common causes include:
- Sudden Stop or Change in Direction: Pivoting quickly on one leg can strain the ACL.
- Direct Impact: A direct hit to the knee, such as in football or hockey, can result in an ACL tear.
- Landing Incorrectly from a Jump: When the foot hits the ground awkwardly, the force can cause the ACL to tear.
- Overextension: Hyperextending the knee beyond its normal range can also lead to an ACL injury.
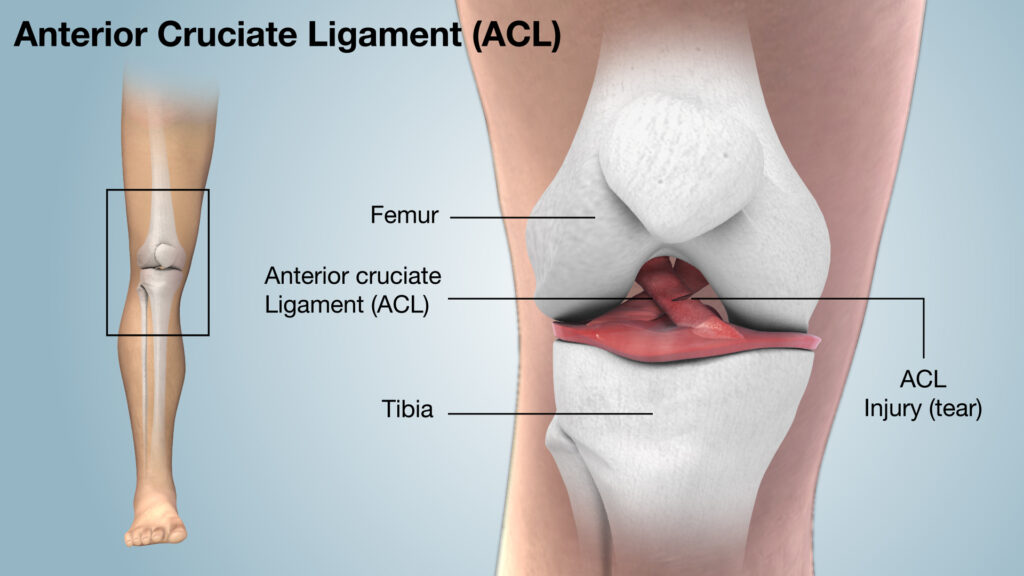
Symptoms of ACL Injury
An ACL injury is usually noticeable immediately. The symptoms include:
- A Popping Sound: Many individuals report hearing or feeling a “pop” in their knee at the time of injury.
- Severe Pain: The pain is often intense and immediate, making it difficult to continue any physical activity.
- Swelling: The knee typically swells within a few hours of the injury.
- Loss of Range of Motion: The injured knee may lose its full range of motion.
- Instability: The knee may feel unstable or give way when you try to stand or walk.
Diagnosis of ACL Injury
If you suspect an ACL injury, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. A specialist like Dr. Kritesh Mishra, a Joint Replacement & Sports Injury Specialist in Meerut, will perform a physical examination to assess the injury. This might include checking for tenderness, swelling, and stability of the knee joint.
In addition to a physical exam, imaging tests such as an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) may be used to get a clearer picture of the extent of the injury. The MRI can help confirm whether the ACL is partially or completely torn and if there are any other associated injuries like damage to other ligaments or the meniscus.
Treatment Options for ACL Injury
Treatment for an ACL injury varies depending on the severity of the injury and the patient’s lifestyle. Here are the main treatment options:
Non-Surgical Treatment: For mild ACL injuries or patients who lead a relatively sedentary lifestyle, non-surgical treatments may be sufficient. These include:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that put stress on the knee.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises for the muscles around the knee to improve stability.
- Bracing: Wearing a knee brace to provide additional support.
Surgical Treatment: In cases of a complete tear or for those who wish to return to sports or physically demanding activities, surgery is often recommended. ACL reconstruction surgery involves replacing the torn ligament with a tissue graft. This surgery is usually followed by a rigorous rehabilitation program to restore strength and function to the knee.
Rehabilitation: Regardless of whether surgery is performed, rehabilitation is a crucial part of the recovery process. It typically involves several months of physical therapy focusing on strengthening the knee, improving flexibility, and gradually returning to normal activities.
Prevention of ACL Injury
While it’s not always possible to prevent an ACL injury, especially in contact sports, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Strengthening Exercises: Focus on strengthening the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings.
- Proper Techniques: Learn and practice proper techniques for jumping, landing, and pivoting.
- Wearing Proper Footwear: Shoes with good support and appropriate traction for your sport can help prevent injuries.
- Using Knee Braces: For those with a previous injury, wearing a knee brace during high-risk activities may provide additional stability.
Conclusion
An ACL injury is a serious condition that can significantly impact your mobility and quality of life. If you suspect an ACL injury, it’s essential to seek prompt medical attention. Dr. Kritesh Mishra, a Joint Replacement & Sports Injury Specialist in Meerut, can provide expert diagnosis and treatment to help you recover and get back to your active lifestyle. Whether through non-surgical means or ACL reconstruction surgery, proper treatment and rehabilitation are key to restoring knee stability and function.
For more information or to schedule a consultation, visit Dr. Kritesh Mishra, Joint Replacement & Sports Injury Specialist in Meerut.
Frequently Asked Questions
Common symptoms include a popping sound at the time of injury, severe knee pain, swelling, loss of range of motion, and knee instability.
In some cases, especially with partial tears or less active individuals, non-surgical treatments like physical therapy and bracing may be effective. However, complete tears often require surgery for full recovery, especially for athletes.
Recovery from ACL surgery typically takes about 6 to 9 months, depending on the individual’s rehabilitation progress and adherence to physical therapy. Athletes may require longer before returning to their sport.