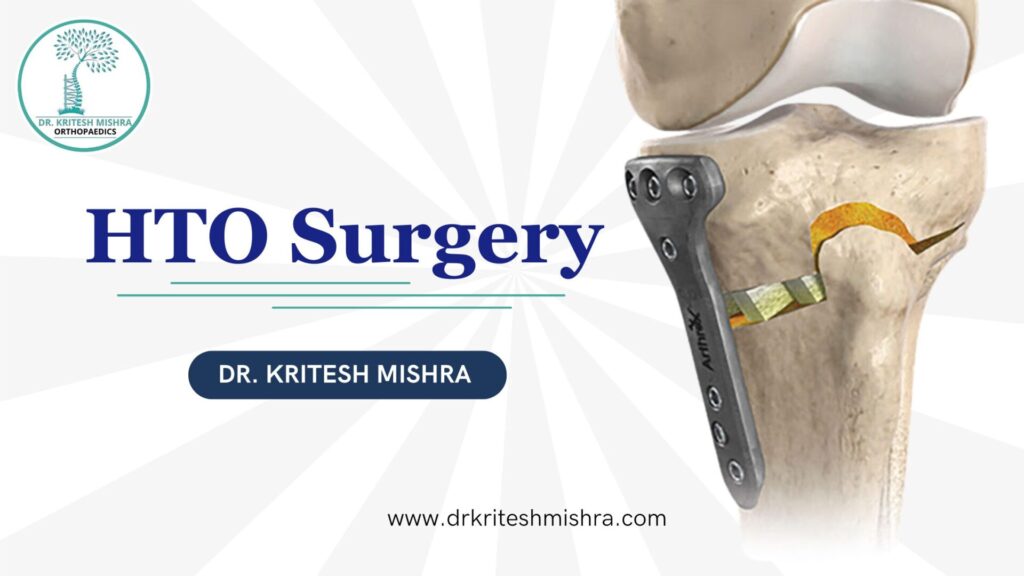
High Tibial Osteotomy (HTO) surgery is a valuable treatment for individuals suffering from knee pain, particularly those with early-stage osteoarthritis or joint issues caused by misalignment. This procedure can help relieve discomfort and delay the need for more invasive surgeries like knee replacement. As a joint replacement and sports injury specialist, I often recommend HTO surgery to patients who want to maintain an active lifestyle while managing knee problems.
In this guide, we’ll explore the basics of HTO surgery, who it’s for, how it works, and what patients can expect during recovery.
What is HTO Surgery?
HTO surgery, or High Tibial Osteotomy, is a surgical procedure designed to realign the knee joint. The main purpose of HTO surgery is to reduce pressure on the damaged or arthritic area of the knee by shifting weight away from the worn-out part of the joint to the healthier, more stable area. This surgery is particularly beneficial for patients with knee problems caused by a misaligned leg, often referred to as “bowlegged” or “knock-kneed” conditions.
By redistributing the load on the knee, HTO surgery can significantly reduce pain, improve knee function, and help delay or even avoid total knee replacement.
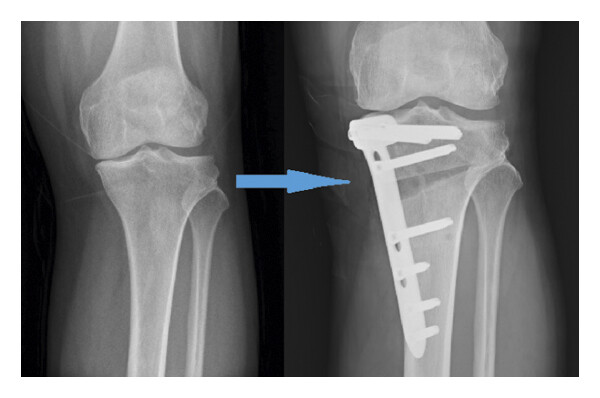
Who is a Candidate for HTO Surgery?
HTO surgery is typically recommended for individuals who experience knee pain due to osteoarthritis or joint degeneration, but are still too young or active for a full knee replacement. The surgery is especially suitable for patients who have cartilage wear on just one side of the knee, rather than damage to the entire joint.
Ideal candidates for HTO surgery include:
- Individuals between 40 to 60 years old
- Patients with good range of motion in the knee
- People who are physically active and want to maintain their mobility
- Individuals with early-stage arthritis localized to one part of the knee
HTO surgery may also be recommended for athletes or people who put significant stress on their knees, as it helps preserve the knee joint for longer periods.
How Does HTO Surgery Work?
HTO surgery involves reshaping and realigning the tibia (shin bone) to shift weight-bearing forces away from the damaged part of the knee. Here’s a breakdown of how the surgery works:
- Planning and Preparation: Before the surgery, detailed imaging like X-rays and MRI scans are used to understand the alignment of the knee joint and the extent of the damage.
- Surgical Procedure: During the procedure, the surgeon makes an incision along the knee and cuts the tibia. Depending on the alignment needed, the surgeon either removes or adds a wedge of bone to the tibia. The bone is then fixed in its new position using metal plates and screws.
- Post-Surgery Alignment: The goal is to shift the alignment of the knee so that the weight-bearing forces are transferred to the healthier part of the joint, reducing pain and wear in the damaged area.
Benefits of HTO Surgery
HTO surgery offers several benefits, especially for individuals with early-stage osteoarthritis or knee misalignment. Some of the key advantages include:
- Pain Relief: By realigning the knee joint, It helps reduce the pressure on the damaged area, providing significant relief from pain.
- Delaying Knee Replacement: This surgery can delay the need for a total knee replacement by preserving the knee joint and prolonging its function.
- Improved Mobility: Patients who undergo surgery often experience improved knee function, allowing them to stay active and continue with activities like walking, running, or sports.
- Joint Preservation: Unlike knee replacement surgery, which involves removing parts of the knee, HTO surgery preserves the natural knee joint, which can be a major advantage for younger patients.
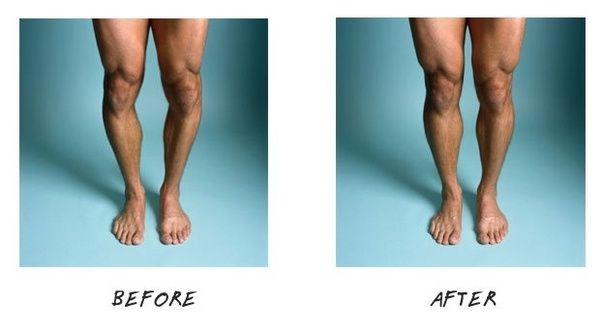
Recovery and Aftercare
The recovery process after surgery requires time, effort, and a commitment to rehabilitation. Here’s what patients can expect during the recovery phase:
- Hospital Stay: Patients usually stay in the hospital for a few days following the surgery to monitor healing and manage pain.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is an essential part of recovery. It helps restore strength, mobility, and range of motion in the knee. Patients typically start with gentle exercises and gradually progress to more intensive activities over time.
- Weight Bearing: Initially, patients may need crutches or a walker to avoid putting weight on the operated knee. Over the course of several weeks, they can slowly begin to bear weight on the knee again.
- Full Recovery: Most patients achieve full recovery within 6 to 12 months, depending on their age, physical condition, and commitment to rehabilitation. However, the pain relief and improved knee function can last for many years after the surgery.
Is HTO Surgery Right for You?
It is a great option for individuals looking to manage knee pain without undergoing knee replacement surgery. If you’re experiencing knee pain due to osteoarthritis or misalignment and want to stay active, consult a specialist to determine whether High Tibial Osteotomy surgery is right for you.
Conclusion
HTO surgery offers an effective solution for knee pain relief and joint preservation, especially for patients with early-stage osteoarthritis or misaligned legs. By redistributing weight on the knee, this procedure can help patients maintain mobility and delay the need for knee replacement. Recovery requires dedication to physical therapy, but the long-term benefits make it worthwhile.
If you’re considering HTO (High Tibial Osteotomy) surgery, reach out to Dr. Kritesh Mishra, Joint Replacement & Sports Injury Specialist in Meerut. With expertise in joint preservation and sports injury treatment, Dr. Mishra can guide you through the process and help you get back to an active, pain-free lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
High Tibial Osteotomy surgery realigns the knee joint by reshaping the tibia to shift weight from the damaged part of the knee to a healthier area, reducing pain and delaying the need for a total knee replacement.
High Tibial Osteotomy surgery is ideal for individuals between 40-60 years old with early-stage osteoarthritis or misaligned knees, who want to relieve pain while maintaining an active lifestyle.
Recovery typically takes 6 to 12 months, with initial rest, followed by physical therapy to restore strength and mobility. Most patients experience long-term pain relief and improved knee function.